Perfect markets achieve efficiency: maximizing total surplus generated. But real markets are imperfect. In this course we will explore a set of market imperfections to understand why they fail and to explore possible remedies including as antitrust policy, regulation, government intervention. Examples are taken from everyday life, from goods and services that we all purchase and use. We will apply the theory to current events and policy debates through weekly exercises. These will empower you to be an educated, critical thinker who can understand, analyze and evaluate market outcomes.


Microeconomics: When Markets Fail
Taught in English
Some content may not be translated
37,191 already enrolled
(609 reviews)
Skills you'll gain
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
15 quizzes
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills


Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 5 modules in this course
In the first part of the course we learnt that if we allow market forces to work we reach an efficient outcome: the maximum benefit that can be generated by a market. The second part of the course explores cases where the markets fail to accomplish our goals. This week sets up the benchmark case of the perfectly competitive market: a model we will modify in the next few weeks. We define Perfect Competition, learn to model it graphically and discuss some key results in terms of long run profits and implications for efficiency.
What's included
20 videos3 quizzes1 discussion prompt
A monopoly is a case where there is only one firm in the market. We will define and model this case and explain why market power is good for the firm, bad for consumers. We will also show that society as a whole suffers from the lack of competition.
What's included
13 videos2 quizzes1 discussion prompt
Monopolies come in various types: one price monopoly, natural monopoly, price discrimination and monopolistic competition. This week we will expand the basic monopoly model to cover these cases and then explore market outcomes in each case. We will also discuss how government may intervene in such cases to benefit society as a whole and increase the surplus generated by the market.
What's included
14 videos3 quizzes1 discussion prompt
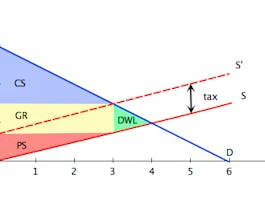
Two classic cases of market failure will be defined and explored: externalities and public goods. We will define each case, demonstrate why the market fails to provide the efficient outcome and suggest interventions through either marked design or regulation.
What's included
20 videos4 quizzes1 discussion prompt
Up to this point we assumed that there is full information in the market. We are now ready to relax this assumption as we introduce the concepts of moral hazard and adverse selection. We learn that asymmetric information may lead to market failure and we discuss some remedies. The last segment in the course is a reminder that besides efficiency, equity is also a criteria we all care about. A short introduction will explore how economist measure poverty and inequality.
What's included
10 videos3 quizzes1 discussion prompt
Instructor

Offered by
Recommended if you're interested in Economics
University of Pennsylvania

Yale University

ESSEC Business School

Rice University
Why people choose Coursera for their career




Learner reviews
Showing 3 of 609
609 reviews
- 5 stars
81.14%
- 4 stars
14.91%
- 3 stars
3.44%
- 2 stars
0.16%
- 1 star
0.32%

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 7,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy
Frequently asked questions
Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the Certificate experience, during or after your audit. If you don't see the audit option:
The course may not offer an audit option. You can try a Free Trial instead, or apply for Financial Aid.
The course may offer 'Full Course, No Certificate' instead. This option lets you see all course materials, submit required assessments, and get a final grade. This also means that you will not be able to purchase a Certificate experience.
When you purchase a Certificate you get access to all course materials, including graded assignments. Upon completing the course, your electronic Certificate will be added to your Accomplishments page - from there, you can print your Certificate or add it to your LinkedIn profile. If you only want to read and view the course content, you can audit the course for free.
You will be eligible for a full refund until two weeks after your payment date, or (for courses that have just launched) until two weeks after the first session of the course begins, whichever is later. You cannot receive a refund once you’ve earned a Course Certificate, even if you complete the course within the two-week refund period. See our full refund policy.