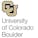The movement of bodies in space (like spacecraft, satellites, and space stations) must be predicted and controlled with precision in order to ensure safety and efficacy. Kinematics is a field that develops descriptions and predictions of the motion of these bodies in 3D space. This course in Kinematics covers four major topic areas: an introduction to particle kinematics, a deep dive into rigid body kinematics in two parts (starting with classic descriptions of motion using the directional cosine matrix and Euler angles, and concluding with a review of modern descriptors like quaternions and Classical and Modified Rodrigues parameters). The course ends with a look at static attitude determination, using modern algorithms to predict and execute relative orientations of bodies in space.


Kinematics: Describing the Motions of Spacecraft
This course is part of Spacecraft Dynamics and Control Specialization
Taught in English
Some content may not be translated

Instructor: Hanspeter Schaub
Top Instructor
23,987 already enrolled
Included with 
Course
(316 reviews)
94%
What you'll learn
Differentiate a vector as seen by another rotating frame and derive frame dependent velocity and acceleration vectors
Apply the Transport Theorem to solve kinematic particle problems and translate between various sets of attitude descriptions
Add and subtract relative attitude descriptions and integrate those descriptions numerically to predict orientations over time
Derive the fundamental attitude coordinate properties of rigid bodies and determine attitude from a series of heading measurements
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
36 quizzes
Course
(316 reviews)
94%
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills

Build your subject-matter expertise
- Learn new concepts from industry experts
- Gain a foundational understanding of a subject or tool
- Develop job-relevant skills with hands-on projects
- Earn a shareable career certificate


Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 4 modules in this course
This module covers particle kinematics. A special emphasis is placed on a frame-independent vectorial notation. The position velocity and acceleration of particles are derived using rotating frames utilizing the transport theorem.
What's included
13 videos3 quizzes
This module provides an overview of orientation descriptions of rigid bodies. The 3D heading is here described using either the direction cosine matrix (DCM) or the Euler angle sets. For each set the fundamental attitude addition and subtracts are discussed, as well as the differential kinematic equation which relates coordinate rates to the body angular velocity vector.
What's included
18 videos1 reading10 quizzes
This module covers modern attitude coordinate sets including Euler Parameters (quaternions), principal rotation parameters, Classical Rodrigues parameters, modified Rodrigues parameters, as well as stereographic orientation parameters. For each set the concepts of attitude addition and subtraction is developed, as well as mappings to other coordinate sets.
What's included
29 videos18 quizzes
This module covers how to take an instantaneous set of observations (sun heading, magnetic field direction, star direction, etc.) and compute a corresponding 3D attitude measure. The attitude determination methods covered include the TRIAD method, Devenport's q-method, QUEST as well as OLAE. The benefits and computation challenges are reviewed for each algorithm.
What's included
13 videos5 quizzes1 peer review
Instructor

Offered by
Recommended if you're interested in Physics and Astronomy
University of Colorado Boulder
University of Colorado Boulder
University of Colorado Boulder
University of Colorado Boulder
Why people choose Coursera for their career




Learner reviews
Showing 3 of 316
316 reviews
- 5 stars
91.45%
- 4 stars
6.96%
- 3 stars
0.94%
- 2 stars
0.63%
- 1 star
0%

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 7,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy
Frequently asked questions
Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the Certificate experience, during or after your audit. If you don't see the audit option:
The course may not offer an audit option. You can try a Free Trial instead, or apply for Financial Aid.
The course may offer 'Full Course, No Certificate' instead. This option lets you see all course materials, submit required assessments, and get a final grade. This also means that you will not be able to purchase a Certificate experience.
When you enroll in the course, you get access to all of the courses in the Specialization, and you earn a certificate when you complete the work. Your electronic Certificate will be added to your Accomplishments page - from there, you can print your Certificate or add it to your LinkedIn profile. If you only want to read and view the course content, you can audit the course for free.
If you subscribed, you get a 7-day free trial during which you can cancel at no penalty. After that, we don’t give refunds, but you can cancel your subscription at any time. See our full refund policy.