We make economics decisions every day: what to buy, whether to work or play, what to study. We respond to markets all the time: prices influence our decisions, markets signal where to put effort, they direct firms to produce certain goods over others. Economics is all around us.


Microeconomics: The Power of Markets
Taught in English
Some content may not be translated
70,958 already enrolled
(1,450 reviews)
Skills you'll gain
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
18 quizzes
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills


Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 5 modules in this course
Where do markets come from? We will start with understanding the constraint of scarcity that we face and the concept of opportunity cost that reflects the true cost of any decision we make. We will learn to model scarcity using the Production Possibilities Frontier that allows us to visualize tradeoffs, distinguish between efficient, inefficient and unattainable points. We will also discuss how economic growth affects our options and allows us to achieve the previously unattainable.
What's included
17 videos2 readings3 quizzes1 discussion prompt
Trade allows us to achieve the unattainable- we can consume more than we can produce on our own. We will introduce the concept of Comparative Advantage and discuss how gains from specialization allow us to use our resources efficiently. We will apply these concepts to a simple model of trade, showing that now the Consumption Possibilities Frontier allows points outside the Production Possibilities Frontier.
What's included
14 videos1 reading2 quizzes1 discussion prompt
We will introduce the central model of Supply & Demand. This will allow you to communicate with other economists and finally understand those business pages and market updates. We will distinguish between a movement along and a movement of the supply & demand curves. We will define market equilibrium as understand that at an equilibrium price there is neither excess demand nor excess supply. We will end by a few scenarios where exogenous changes affect supply and/or demand and analyze the impact on equilibrium price and quantity.
What's included
15 videos1 reading4 quizzes1 discussion prompt
There is a lot of terminology this week. We will introduce of the concept of elasticity of demand that measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in the price of a good. We will explore the relationship between change in price and revenue or sales and how elasticities can help us predict whether a decrease in price will increase or decrease revenue. We then introduce other elasticities of note: cross price elasticity, income elasticity and elasticity of supply. We end the week by exploring the great accomplishment of markets: maximizing the size of the pie or the total benefit to society.
What's included
23 videos1 reading4 quizzes1 discussion prompt
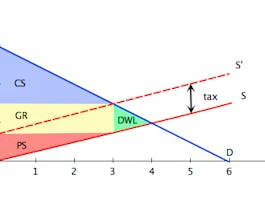
In week four we learnt that the markets maximize the surplus that can be generated. So what happens if the government steps in and intervenes in the market? This week we will analyze price floors and ceilings, taxes and subsidies and learn how the best intentions sometimes lead to very unfortunate results.
What's included
16 videos1 reading5 quizzes1 discussion prompt
Instructor

Offered by
Recommended if you're interested in Economics
University of Pennsylvania

University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign

Rice University
University of Amsterdam
Why people choose Coursera for their career




Learner reviews
Showing 3 of 1450
1,450 reviews
- 5 stars
78.82%
- 4 stars
17.65%
- 3 stars
2.68%
- 2 stars
0.48%
- 1 star
0.34%

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 7,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy
Frequently asked questions
Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the Certificate experience, during or after your audit. If you don't see the audit option:
The course may not offer an audit option. You can try a Free Trial instead, or apply for Financial Aid.
The course may offer 'Full Course, No Certificate' instead. This option lets you see all course materials, submit required assessments, and get a final grade. This also means that you will not be able to purchase a Certificate experience.
When you purchase a Certificate you get access to all course materials, including graded assignments. Upon completing the course, your electronic Certificate will be added to your Accomplishments page - from there, you can print your Certificate or add it to your LinkedIn profile. If you only want to read and view the course content, you can audit the course for free.
You will be eligible for a full refund until two weeks after your payment date, or (for courses that have just launched) until two weeks after the first session of the course begins, whichever is later. You cannot receive a refund once you’ve earned a Course Certificate, even if you complete the course within the two-week refund period. See our full refund policy.